模式切换
异常处理
异常处理是 Java 语言中的一个重要机制,用于捕获和处理程序在运行时发生的错误,避免程序异常终止,提高程序的健壮性和可靠性。
异常概述
在 Java 中,异常(Exception)是指程序在运行时发生的不正常情况,它可能由程序错误、硬件故障、网络问题或其他外部因素引起。Java 提供了异常处理机制,使程序能够在发生异常时采取适当的措施,而不是直接终止。
Java 的异常类层次结构如下:
- Throwable(所有异常的根类)
- Error(错误,程序无法处理)
- Exception(异常,可捕获和处理)
- 编译时异常(Checked Exception)
- 运行时异常(Unchecked Exception / Runtime Exception)
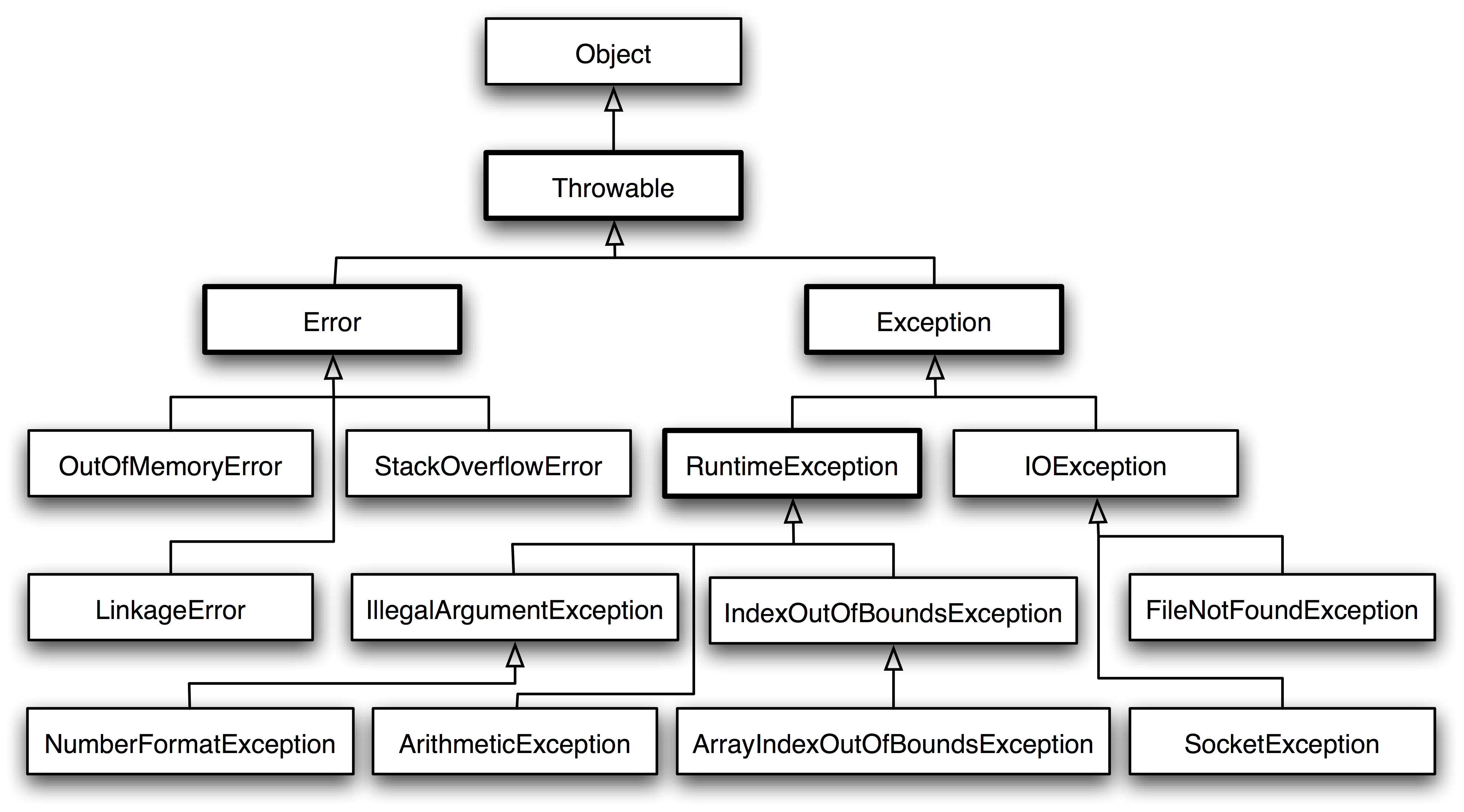
图 Java 异常类层次结构
示例:
java
try {
int result = 10 / 0; // 发生异常
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到异常: " + e.getMessage());
}处理程序异常错误
错误(Error)
Error 是 Java 的一种严重错误,通常由 JVM 本身抛出,例如:
OutOfMemoryError(内存溢出)StackOverflowError(栈溢出)
示例:
java
public class StackOverflowDemo {
public static void recursiveMethod() {
recursiveMethod(); // 无限递归,导致 StackOverflowError
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
recursiveMethod();
}
}捕捉异常
Java 提供了 try-catch-finally 语句来捕获并处理异常:
java
try {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(numbers[5]); // 数组越界异常
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("异常发生: " + e);
} finally {
System.out.println("执行 finally 代码块");
}Java 常见异常
| 异常类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
NullPointerException | 访问 null 对象的方法或属性 |
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 数组索引越界 |
ArithmeticException | 算术错误,如除零 |
IOException | 输入输出异常 |
ClassNotFoundException | 类未找到 |
FileNotFoundException | 文件未找到 |
IllegalArgumentException | 非法参数 |
示例:
java
public class NullPointerExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length()); // NullPointerException
}
}自定义异常
Java 允许开发者创建自定义异常,以满足特定的业务需求。
示例:
java
// 自定义异常类
class AgeException extends Exception {
public AgeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
// 使用自定义异常
public class CustomExceptionDemo {
public static void checkAge(int age) throws AgeException {
if (age < 18) {
throw new AgeException("未成年人不允许注册!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
checkAge(16);
} catch (AgeException e) {
System.out.println("异常捕获: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}在方法中抛出异常
使用 throws 关键字抛出异常
当一个方法可能会抛出异常时,需要在方法签名中使用 throws 声明。
示例:
java
public void readFile(String filePath) throws IOException {
FileReader file = new FileReader(filePath);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(file);
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
}使用 throw 关键字抛出异常
throw 关键字用于在方法内部手动抛出异常。
示例:
java
public void checkNumber(int num) {
if (num < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("数字不能为负数!");
}
}运行时异常
运行时异常(RuntimeException)是 Exception 的子类,通常由程序错误引起,不需要强制捕获或声明 throws。
示例:
java
public class RuntimeExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 0;
int result = a / b; // ArithmeticException: / by zero
}
}异常的使用规则
- 优先使用
try-catch-finally处理异常 throws关键字声明可能抛出的异常throw关键字手动抛出异常- 捕获多个异常时,子类异常需放在前面
- 避免滥用
catch (Exception e) - 确保
finally代码块执行 - 优先使用
日志记录异常
示例(捕获多个异常):
java
try {
int[] arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 10; // 发生异常
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组索引越界异常: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("其他异常: " + e.getMessage());
}